Testing your app
SwiftWasm supports both swift-testing and XCTest for writing test suites. Your project needs to have a
Package.swift package manifest with test targets configured. Please follow our SwiftPM guide for new projects.
Testing in JavaScript environments
If you’re building a SwiftWasm app that runs in JavaScript environments (browsers or Node.js), you can use JavaScriptKit’s testing utilities to run your tests directly in those environments. For detailed information on how to set up and run tests in JavaScript environments, please refer to the JavaScriptKit Testing documentation.
Standalone testing with WASI
If you prefer to run tests in a standalone environment without JavaScript, you can use WASI-compatible runtimes as described below.
Make sure your Package.swift has test targets configured. For example:
Note that swift test doesn’t work for WebAssembly targets. Building tests and running them are two separate steps. After building your tests, you can use a WASI-compatible host such as wasmtime or WasmKit to run the test bundle.
targets: [
.target(name: "Example"),
.testTarget(name: "ExampleTests", dependencies: ["Example"]),
]
Running swift-testing suites
For running swift-testing test suites, please refer to the swift-testing WASI documentation.
Running XCTest suites
You can build your XCTest suite by running this command in your terminal:
$ swift build --build-tests --swift-sdk $SWIFT_SDK_ID
After building, run the test bundle with a WASI runtime. For example, with wasmtime:
$ wasmtime --dir . .build/wasm32-unknown-wasip1/debug/ExamplePackageTests.wasm
Or with WasmKit:
$ wasmkit run --dir . .build/wasm32-unknown-wasip1/debug/ExamplePackageTests.wasm
(--dir . is used to allow XCTest to find Bundle.main resources placed alongside the executable file.)
As you can see, the produced test binary starts with the name of your package followed by
PackageTests.wasm. It is located in the .build/wasm32-unknown-wasip1/debug subdirectory, or in the .build/wasm32-unknown-wasip1/release
subdirectory when you build in release mode.
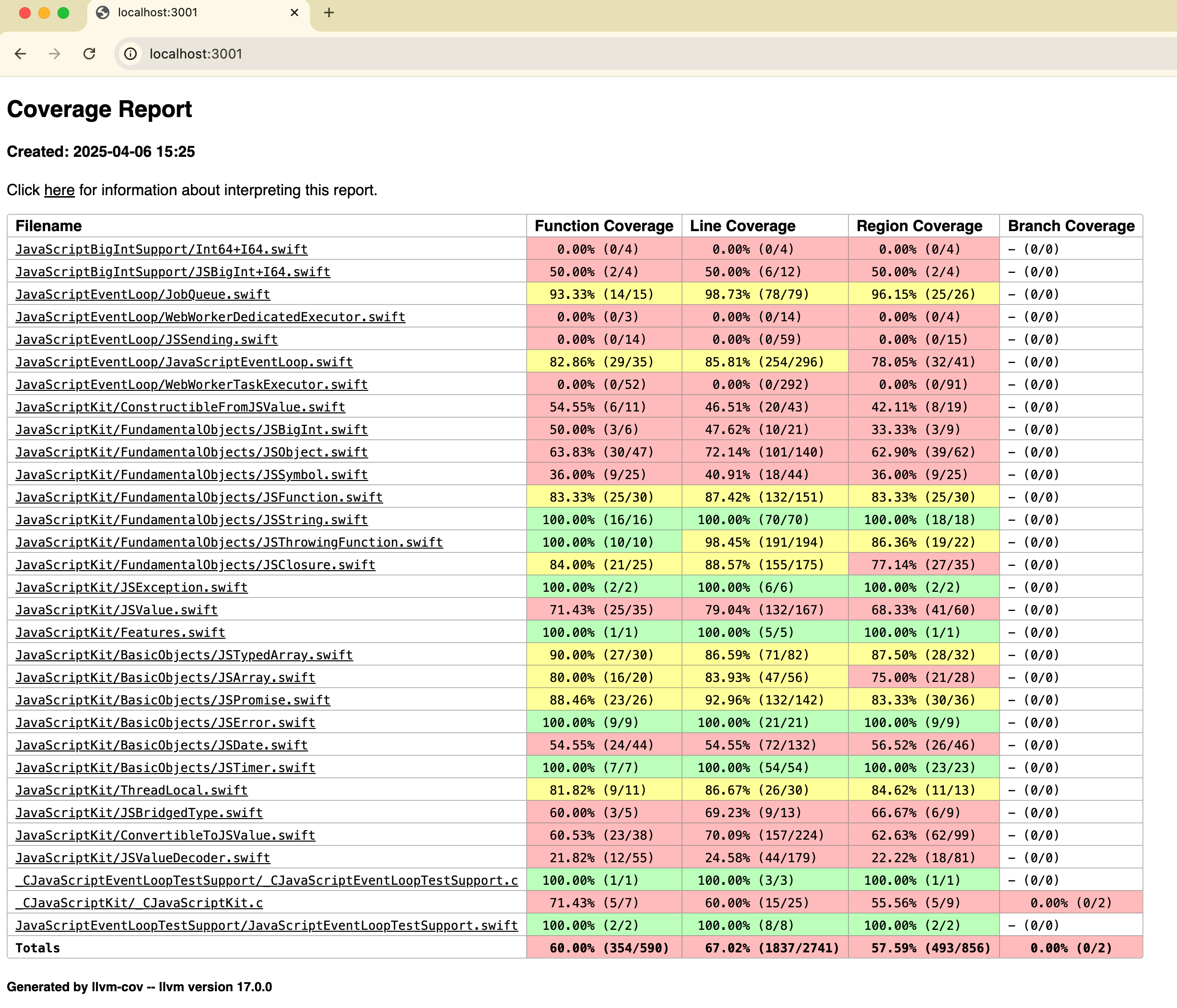
Code coverage
Note: Code coverage support is available only in 6.1 and later.
You can also generate code coverage reports for your test suite. To do this, you need to build your
test suite with the --enable-code-coverage and linker options -Xlinker -lwasi-emulated-getpid:
$ swift build --build-tests --swift-sdk $SWIFT_SDK_ID --enable-code-coverage -Xlinker -lwasi-emulated-getpid
After building your test suite, you can run it with a WASI runtime (e.g., wasmtime or WasmKit) as described above. The raw coverage
data will be stored in default.profraw file in the current directory. You can use the llvm-profdata
and llvm-cov tools to generate a human-readable report:
$ wasmtime --dir . .build/wasm32-unknown-wasip1/debug/ExamplePackageTests.wasm
$ llvm-profdata merge default.profraw -o default.profdata
$ llvm-cov show .build/wasm32-unknown-wasip1/debug/ExamplePackageTests.wasm -instr-profile=default.profdata
# or generate an HTML report
$ llvm-cov show .build/wasm32-unknown-wasip1/debug/ExamplePackageTests.wasm -instr-profile=default.profdata --format=html -o coverage
$ open coverage/index.html